The hormone that indicates the onset of pregnancy, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), is produced soon after a fertilized egg implants in the uterus. I’ll provide useful hints on early pregnancy developments at the beta-hCG test.
Is your hCG off the scale? Thinking you may be pregnant with twins? Admittedly, twins often have higher beta hCG levels compared to singleton pregnancies, but this is not a failsafe. An ultrasound is the most reliable way to verify that twins are on the way.
This article will look at what beta hCG is, the difference in levels between twin and singleton pregnancy, why hCG by itself can not confirm twins, patterns you shouldn’t ignore, other reasons to have a high hCG, and some real-life examples. There will also be a beta hCG twins chart to compare week-by-week ranges.
What is Beta hCG?
Beta hCG or human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone secreted by the placenta soon after fertilization takes place and results in the attachment of an egg to the lining of the uterus. It is used when helping an early pregnancy because it ensures the persistence of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone.
There are two main types of hCG tests:
- Qualitative hCG test – This involves a simple yes-or-no pregnancy screening to check the presence of hCG in urine or blood, whose results do not reveal the amount of the hormone or the stage of the pregnancy.
- Quantitative (beta) hCG test – Determines the right hCG measurements in the bloodstream and gives much comprehensive details that are necessary when conducting health checks on pregnancies, spotting abnormalities, and following the baby’s development over time.
During early pregnancy, one of the tools doctors can use to determine whether the pregnancy is normal or not is the presence of beta-hCG. They aid in monitoring trends of growth and signs of complications, and they even indicate an early signal of the level of beta-hCG in twin pregnancies in certain instances.

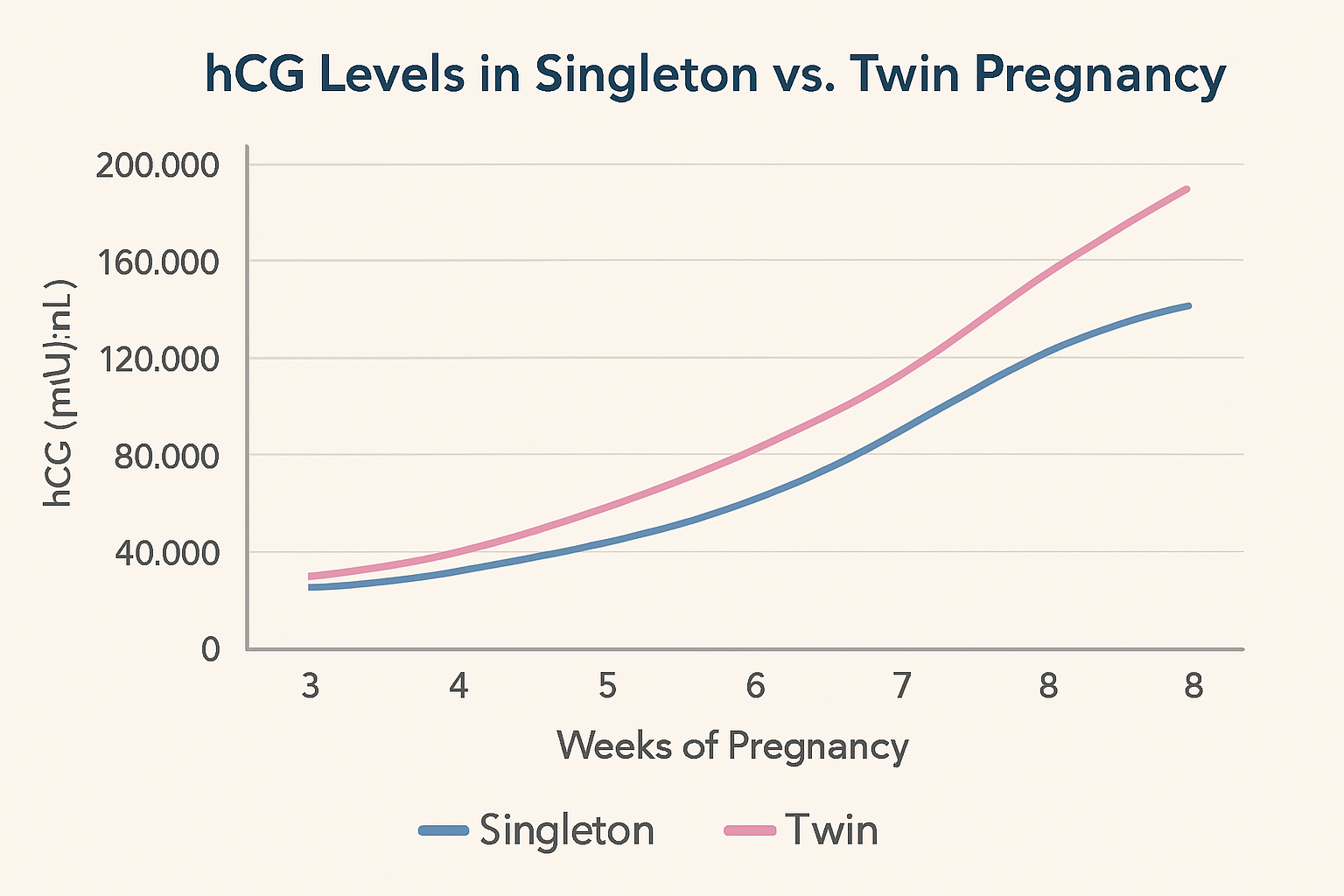
Beta hCG Levels in Twin vs. Singleton Pregnancies
The twins’ hCG levels range between 30 percent and 50 percent greater than those of a singleton pregnancy in most cases. This occurs due to the higher hCG production of two embryos in comparison to a single embryo. Although such differences may be observable, the ranges overlap to a large extent, and thus, high hCG levels are not sufficient to make a diagnosis. Here’s a beta hCG twins chart comparing singleton and twin ranges during weeks 3–8:
Week-by-Week Beta hCG Ranges
| Week | Singleton hCG Range (mIU/mL) | Twins hCG Range (mIU/mL) |
| 3 | 5 – 50 | 10 – 100 |
| 4 | 5 – 426 | 200 – 7,000 |
| 5 | 18 – 7,340 | 1,000 – 10,000 |
| 6 | 1,080 – 56,500 | 7,000 – 200,000 |
| 7–8 | 7,650 – 229,000 | 30,000 – 400,000+ |
An example is that a reading of 20,000 mIU/mL at week 6 may indicate a twin pregnancy; however, it may also fall within the upper range of a singleton. Normal values of beta-hCG in twins may be elevated, but are not limited to multiplex cases.
The major lesson to be learned here is that numerically indicative numbers may raise suspicion; however, they should be interpreted in conjunction with ultrasound and clinical findings.
Why You Can’t Rely on hCG Alone for Diagnosing Twins
An elevated level of hCG might prompt one to consider twins; however, a single reading cannot be conclusively attributed to twins. High levels can vary widely between pregnancies for several reasons.
The process of ovulation has the capability of displacing the levels of hormone later or earlier than anticipated; the implantation window of the embryo also influences the time at which the production of hCG commences.
There are also variations in the quantity of the hormone produced, depending on the different forms of multiple gestation, such as identical and fraternal twins. These variables overlap with singleton pregnancies, and therefore, relying solely on hCG can be inaccurate.
Ultrasound is the primary means of confirming a twin pregnancy and is typically performed between weeks 6 and 7, when the two gestational sacs or heartbeats are visible.
In fact, as most ob-gyns remark, hCG proclaims that you are pregnant, but an ultrasound informs you about the number of pregnancies. This is to make a correct diagnosis and make informed guesses based on laboratory values alone.
Twin Pregnancy Beta hCG: Trends Matter More Than Numbers
Instead of focusing on a single figure, physicians consider the rate of doubling; hCG typically doubles every 48 to 72 hours during pregnancy. There is a possibility of a twofold increase in twin pregnancies, although this is not necessarily the case.
Sample Twin hCG Trend (Early Weeks):
- Day 14 post-ovulation: 150 mIU/mL
- Day 16: 320 mIU/mL
- Day 18: 720 mIU/mL
- Day 20: 1,600 mIU/mL
Following trends will enable the detection of healthy development, whether in a singleton pregnancy or multiple pregnancies.
What Else Can Cause High Beta hCG?
High beta hCG doesn’t always mean twins. Other possible causes include:
- Molar pregnancy – An unusual circumstance in which abnormal placental tissue is formed instead of a normal pregnancy, resulting in very high alpha hCG levels, where necessary medical examination shall be done to ensure an average treatment is rendered.
- Miscalculated gestational age – Your pregnancy may be farther along than is thought because of an earlier ovulation or implantation, so your beta hCG levels may also be higher naturally during testing as a result.
- Certain medical conditions – Health conditions, such as kidney disease, hormone-producing disorders, could increase beta hCG levels, producing results which are similar to seeing in multiple pregnancies, including twins.
- Rare hCG-producing tumors – Rare types of tumors, e.g., choriocarcinoma, may produce elevated levels of beta hCG, which may give a false-positive pregnancy hormone test result that necessitates a prompt diagnostic investigation and therapy.
When and How to Test for hCG Accurately
Fourteen days or more after ovulation have been tested to generate minimal false negatives, or results that can give a false impression.
The same laboratory should be used for all beta hCG tests to enable tracking of trends. Overall, slight differences in measurement approaches applied by different labs can lead to variation.
A transvaginal ultrasound is the most reliable method to detect a twin pregnancy when the level of beta hCG exceeds a particular level (approximately 1,500-2,000 mIU/mL).
Real-Life Twin Pregnancy hCG Case Studies
- Case Study 1 – Patient A had a beta-hCG level of 8,500 mIU/mL at 5 weeks. Two days later, the repeat test was 17,000 mIU/mL. At week 6, an ultrasound showed two heartbeats in the case of fraternal twins.
- Case Study 2 – The beta hCG of patient B at the 4th week was 950 mIU/mL and doubled quickly to 2,000 mIU/mL after 2 days. At week 7, it was identified using ultrasound that it was one set of identical twins sharing a placenta.
These examples illustrate both the matching and the differences that can exist between singleton and twin hCG levels, and how the final stage is always confirmed by ultrasound.
FAQs
Can high beta hCG mean twins?
Yes, twins can be indicated by high beta-hCG, but this is not conclusive. Levels may range widely, and a multiple pregnancy condition can only be confirmed by ultrasound.
How early can hCG detect twins?
Twin pregnancies may experience a faster increase in beta-hCG, and confirmation is usually done between the 6th and 9th week using ultrasound, where both fetal sacs or embryos can be distinctly identified.
What is a normal beta hCG for twins at 5 weeks?
Normal beta-hCG levels at 5 weeks are approximately 200 to 10,000 mIU/mL in twins and can be considerably overlapped by singleton pregnancies, which can make diagnosis difficult.
Do fraternal twins produce more hCG than identical twins?
No, fraternal twins do not always cause a higher level of hCG compared to identical twins. The types of twins do not correlate as much as the concentration of hormones because of the activity of the placenta and pregnancy-specificities.
Conclusion
A close association with twins and the determination of beta-hCG levels may be a cumulative indicator, but it is not sufficient for a conclusive diagnosis.
Although hCG levels are usually higher in pregnancies with twins compared to those with singletons, numerous other factors also affect the results, including ovulation and implantation.
The more time to track the rate of doubling, the better. Finally, the multiple pregnancy may be confirmed only with the help of an ultrasound.
When your hCG levels appear unexplainably elevated, speak with your healthcare provider about serial testing and early imaging to gain a better understanding and relief.
Also Check: How Many Times Can You Donate Eggs