The doctors would typically prefer a uterine lining of around 7 to 8 millimeters when one wants to become pregnant or before going through the IVF procedure. This thickness facilitates the embryo’s implantation well. Not all women can achieve this goal easily, and this can be frustrating and confusing.
This guide will come to your rescue as it integrates recognized expertise with genuine patient testimonies who have passed through the same. Together, we will also explore safe and effective methods for naturally and medically supporting the body in maintaining a healthy uterine lining, which can lead to improved fertility outcomes.
Why Thickness Matters — Ideal Metrics vs. Outcomes
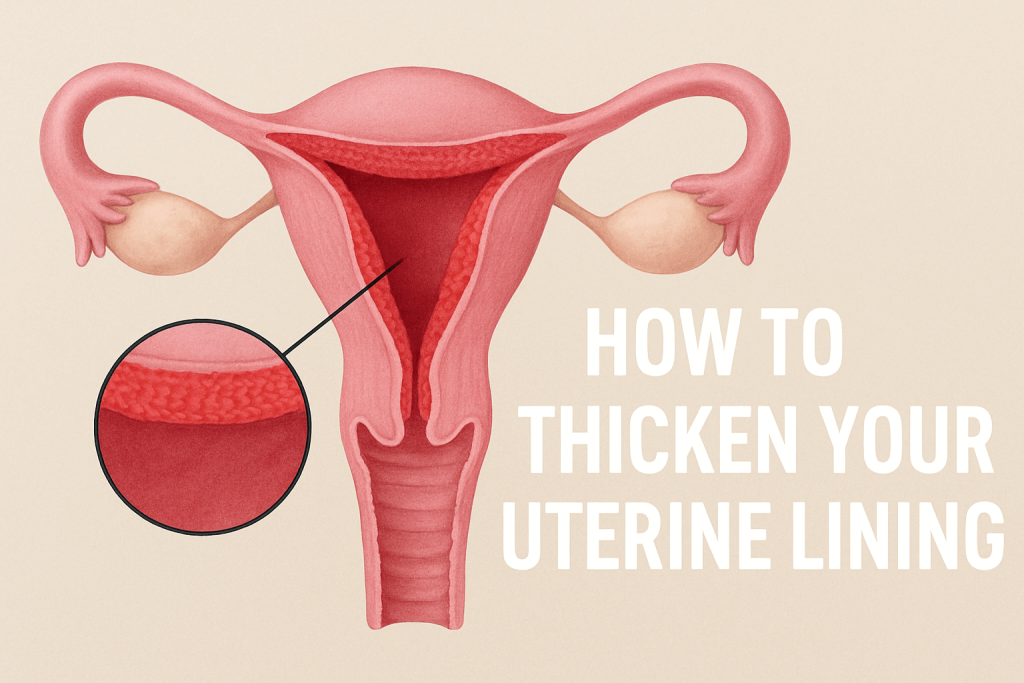
The innermost layer of the uterus is the endometrium, the uterine lining that gets ready to receive a fertilized egg every month. Thickness is a critical issue, as it has a direct impact on implantation success.
Alife Health’s 2021 survey found indicate that a thicker endometrium at the point of embryo transfer, of at least 7 mm, likely correlates with higher rates of pregnancy. A thickness less than this benchmark can lower the chances of implantation.
But thickness does not always constitute everything. Investigations have shown that blood circulation, the quality of the lining, and hormonal balance also play their roles.
As an example, even women with a thin endometrium can achieve a successful pregnancy, and it is essential to remember that the health of the endometrium is complex. Nevertheless, the commonly accepted clinical mark to optimize fertility is the 7–8 mm range.
Natural Methods Backed by Research
Natural measures to thicken the endometrium are often the first choice for many women before resorting to medical treatment. The following are some of the highly researched strategies:
- L-Arginine: This amino acid promotes the synthesis of nitric oxide, which stimulates increased blood circulation in the uterus. A research article on Fertility and Sterility in 2014 showed that women who introduced supplements containing 6 grams of supplements daily showed better endometrial development. On anecdotal evidence, a single anonymous Redditor said that the addition of L-Arginine had produced a difference after roughly two cycles of use.
- Vitamin E: Vitamin E is known because of its antioxidant abilities that have the potential to increase the flow of blood in the uterus. Research suggests that 400 IU of the supplement could be beneficial to maintain lining thickness in good health daily. A case in point of a patient who has undergone this: I have already found my lining better since I started taking vitamin E regularly, and this was within two months.
- Diet and Foods for a Healthy Uterine Lining: A highly nutritious diet is healthy for the endometrial health. Foods with a high level of omega-3 (including salmon), green vegetables, and iron should be stressed. The nutrients support the blood supply to the uterus and aid in tissue repair.
- Exercise: Moderate exercise improves circulation. Moderate exercise, such as walking or yoga, can help improve uterine blood flow and reduce pressure on the body.
- Heating Packs: Heat to help the localized blood circulation in the lower abdomen. When using this approach, some women find it useful; such practices may also occur alongside other activities.
- Acupuncture: Multiple research studies indicate that acupuncture can improve blood flow in the uterus and the thickness of the uterine lining, possibly due to hormonal normalization and reduced stress levels. The common regimens include weekly protocols in the follicular phase.
These natural choices are mostly safe, though they are to be discussed with your healthcare provider, especially in case you are under fertility treatment.
Medical Interventions
Medical treatments can play an important role when it comes to helping those people who require more action than what is supplied by nature alone:
- Estrogen Protocols: Estrogen triggers the thickening of the endometrium. Oral, transdermal, or injectable estrogen is often used. Transdermal patches can lead to endometrial growth with fewer side effects, According to a 2019 PMC study that notes that protocols vary.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): PRP utilizes the concentrated platelets contained in your blood, which are injected into the uterus, to induce tissue regeneration. Early research reports are showing promising results of improvement in endometrial thickness and pregnancy rates, particularly among women with thin endometria and those who have failed to respond to other treatments.
- Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF): The endometrial growth can be stimulated by this growth factor. The clinical trials are mixed, but patients with refractory thin lining improvement are seen.
- Sildenafil (Viagra): Uterine blood flow can be enhanced by increasing blood flow to the blood vessels through sildenafil. The dosage is dependent, but initially, the dosage is 25 mg vaginally, once daily.
- Growth Hormone (GH): Alternatively, GH is adjunctively administered during IVF to enhance uterine receptivity and endometrial thickness.
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG): It is exploited to aid the luteal phase and receptivity of the endometrium in the IVF cycle.
- Aspirin: Some studies suggest that low-dose aspirin may improve blood flow to the uterus and reduce clotting, which could support implantation.
However, evidence is mixed, and many fertility specialists only recommend it in specific cases, such as for patients with certain clotting disorders. Always discuss this option with your doctor before use.
All these interventions have their protocols and differ in the level of evidence. Your fertility specialist can assist in customizing treatments to meet your specific needs and reactions.
Natural vs. Medical Options for Uterine Lining Support
| Approach | Method | Evidence Level | Potential Benefits | Considerations |
| Natural | L-Arginine | Moderate (some human studies) | Improves blood flow to uterus | May need 2–3 cycles for effects; check for blood pressure issues |
| Vitamin E | Moderate | Antioxidant, improves uterine blood flow | High doses can interact with blood thinners | |
| Diet (omega-3, leafy greens, iron) | Strong for general health | Supports blood supply and tissue repair | Requires consistent intake over months | |
| Exercise (walking, yoga) | Moderate | Enhances circulation, reduces stress | Avoid high-intensity if in treatment | |
| Heating packs | Low (anecdotal) | Promotes local blood flow | Use with caution to avoid burns | |
| Acupuncture | Moderate | May normalize hormones, improve flow | Works best in combination with other methods | |
| Medical | Estrogen therapy | Strong | Directly stimulates endometrial growth | Monitor for side effects; protocols vary |
| PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) | Emerging | Regenerates uterine tissue | Limited but promising studies; procedural cost | |
| G-CSF | Mixed | Stimulates lining growth | Not effective for all; more research needed | |
| Sildenafil (Viagra) | Mixed | Increases uterine blood flow | Vaginal or oral; must be prescribed | |
| Growth Hormone | Limited | May enhance receptivity | Usually adjunct to IVF; costly | |
| HCG | Mixed | Improves luteal phase support | Only in IVF context | |
| Low-dose aspirin | Mixed/controversial | May improve circulation and reduce clotting | Only in select cases; consult doctor |
Patient Voices
The context of these methods is very valuable when it comes to the real patient experience. In various forums on Reddit, people talk about their experiences:
- I had tried vitamins and acupuncture with not much success, so my doctor recommended PRP. One user wrote: I ended up with a lining of 8 mm after two cycles had passed.”
- One said, L-Arginine worked, but I needed to take it along with estrogen therapy to see an improvement.”
- It is also common to hear the caution: Be cautious with aspirin and supplements; always consult your doctor. What I experienced is the side effects of self-medication.”
The narrations act as an illustration of the trial-and-error factor that numerous individuals have to undergo. The best combination is the multidisciplinary approach with medical consultation and guidance.
Clinic Insights
Most fertility clinics usually have a mix of natural and medical treatments. The success rates (undocumented) vary widely at local centers, with implantation success reported of up to 70 percent at selected clinics after the implementation of PRP or tailored estrogens in patients where the lining is so thin.
Differing protocols are applied; the most publicized of those include the close monitoring lining under ultrasound during stimulation, adjusting any medication according to response, and offering additional treatment measures, including acupuncture or dietary supplementation.
Clinics observe that the individual treatment regimes play a critical role since the causes of the thin uterus lining may be a result of hormonal disorders, scarring, or inflammation.
FAQs
What is a healthy uterine lining measurement before IVF?
It is suggested that the ideal thickness of the uterus lining before an IVF is 7-14 millimetres, which is considered to be friendly to the successful implantation of the embryos and the subsequent chance of receiving a pregnancy.
How long before IVF should I start supplements?
Supplements like L-Arginine and Vitamin E work best when started 3–4 months before IVF, giving the lining time to grow and improve in quality.
When is PRP recommended?
PRP should be utilized when the uterine lining is thin in women and has not responded to conventional methods such as estrogen therapy, and when such patients are planning to transfer embryos in IVF cases
Conclusion
A balanced diet of cure and prevention solutions on how to safely increase the thickness of your uterine lining. The parental chance of having a 7-8 mm lining would improve the chances of implantation and fertility rate.
Meeting a fertility consultant allows one to be assisted in a personalized manner. The key step forward is the right guidance and proper patience, as well as evidence-based practices.
Also Check: Twins and Beta hCG Levels